Command Workflows: Supercharge Your Content Creation with Markdown, Obsidian, and VS Code
Automate Your Content Workflows
Automate your content workflows with AI in your terminal. Command integrates seamlessly with Markdown, Obsidian, and VS Code:
$ ask "create a table of planets"
# Streaming response from Claude Sonnet 4.5...
| Planet | Distance from Sun | Diameter | Moons |
|----------|------------------|-------------|--------|
| Mercury | 57.9 million km | 4,879 km | 0 |
| Venus | 108.2 million km | 12,104 km | 0 |
| Earth | 149.6 million km | 12,742 km | 1 |
| Mars | 227.9 million km | 6,779 km | 2 |
$ cmnd test ask
✓ Claude Sonnet 4.5: 1.2s (fast)
✓ GPT-4o: 1.8s (accurate)
✓ Gemini Flash: 0.8s (ultra-fast)Command
Turn your Terminal into a configurable AI workspace with 15+ LLMs and 7 providers. Intent-driven workflows with markdown integration.
- 15+ models: Claude, GPT-4o, Gemini, Groq, Ollama
- Intent-driven workflows with VS Code & Obsidian
- Model testing, trends visualization, audit trail
Transform Partial Ideas into Complete Content
One of Command’s most powerful features is its ability to expand partial content into complete, well-researched material. Write partial blog posts, seed ideas, intent lists, or incomplete notes—then use Command to expand them into finished content.
This workflow transforms how knowledge workers create content, turning hours of writing into minutes while maintaining quality and consistency.
The refer Command: Your Content Expansion Engine
The refer command works with custom refer-section configs in command.yml to transform partial content into complete posts, notes, articles, or research papers. You can:
- Experiment with different models
- Tune settings by document type
- Define custom folders for organization
- Specify document-specific system prompts
Example: Expanding Blog Posts
Let’s say you have a partially written blog post on startup growth strategies in your Posts folder. Here’s the related config section using Claude Opus 4.1 for creative writing:
refer-post-to-update:
lookup-folder: Posts
max-tokens: 4000
model: opus4-1 # Optimized: Opus 4.1 excels at creative writing
provider: claude
save: true
save-folder: Posts
system: You will be given a partially written blog post on a topic.
Your job as an expert blog writer is to expand the post
with well-researched content, engaging examples, and actionable insights.
Maintain the author's voice and style while adding depth and polish.
temperature: 0.5Run the command and watch as the model streams its response:
refer post-to-update "startup-growth-hacking"The expanded post saves to the Posts folder with an updated prefix, preserving your original.
Create Custom Document Types
Want to process research papers, class notes, or cooking recipes? Just copy and customize a refer-* section:
Research Paper Summaries
refer-paper-to-summarize:
lookup-folder: Papers
max-tokens: 2000
model: sonnet4-5 # Sonnet 4.5 for technical analysis
provider: claude
save: true
save-folder: Summaries
system: Summarize this research paper, focusing on methodology,
key findings, and implications. Include citations and limitations.
temperature: 0.3Meeting Notes Expansion
refer-notes-to-expand:
lookup-folder: Notes
max-tokens: 4000
model: haiku4-5 # Haiku 4.5 is fast and cost-effective
provider: claude
save: true
save-folder: Notes/Expanded
system: Transform these raw meeting notes into a structured document
with clear action items, decisions made, and follow-up tasks.
temperature: 0.3Then run your custom command:
refer notes-to-expand "weekly-standup-2025-10-15"Model Selection Best Practices
Different content types benefit from different models:
- Haiku 4.5: Simple extraction, templates, summaries (fast, 40% cheaper)
- Sonnet 4.5: Complex analysis, technical writing, code generation
- Opus 4.1: Creative writing, deep research synthesis, content expansion
Combining Commands for Powerful Workflows
Command becomes even more powerful when you combine multiple commands. Here’s a complete workflow for generating comprehensive content:
Step 1: Define Your Document Template
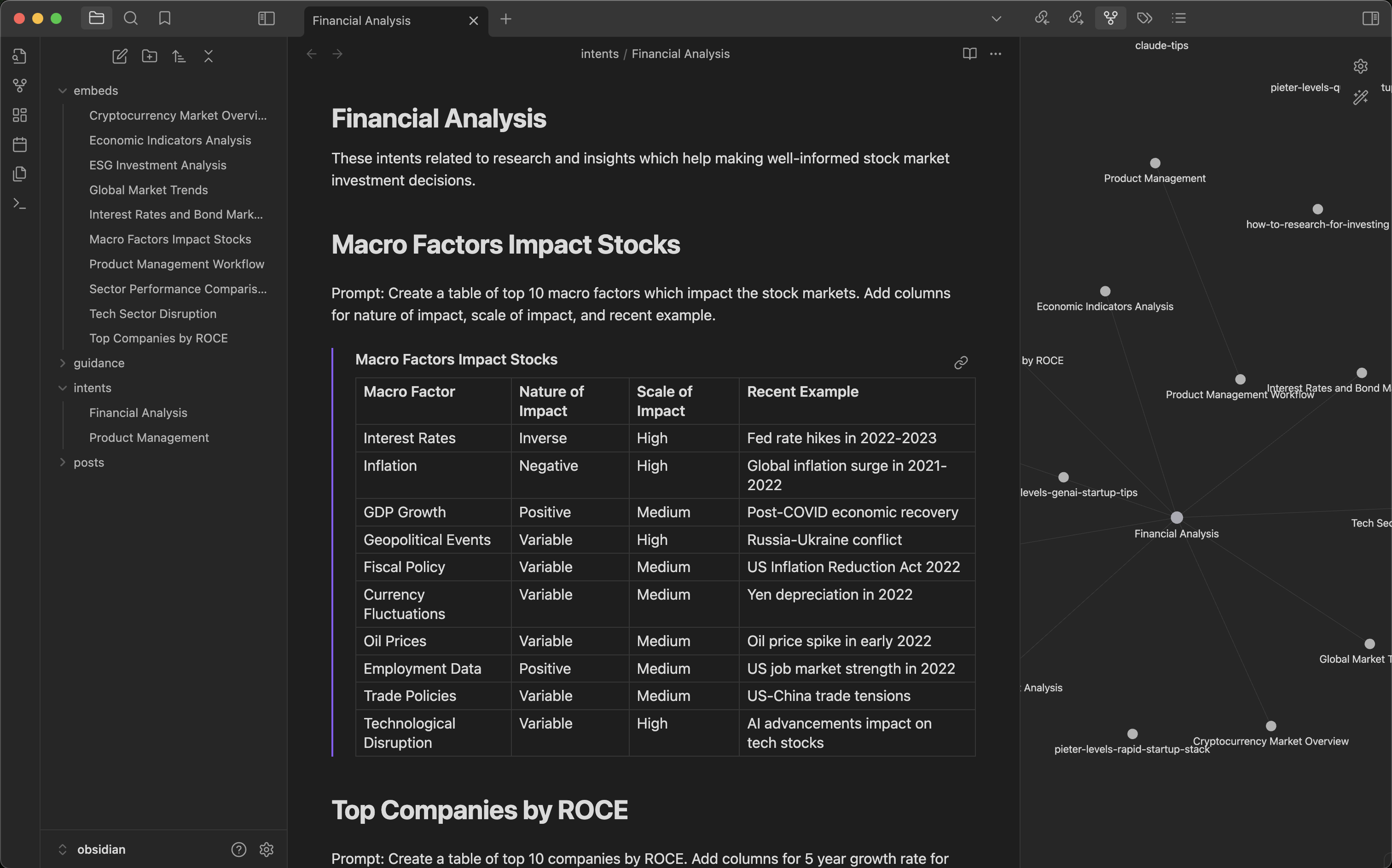
Create a markdown template for a set of intents. For example, Financial Analysis.md or Product Management.md. Add a few intents as headings:
# Financial Analysis
## Macro Factors Impact Stocks
[Prompts to analyze macro economic factors]
## Top Companies by ROCE
[Prompts to identify high-return companies]
## Tech Sector Valuation
[Prompts to analyze tech valuations]Step 2: Expand Intents
Use Command to brainstorm more related intents and prompts:
refer intents-to-expand "Financial Analysis"The model will add more relevant intents and prompts to your template.
Step 3: Generate Content Embeds
Now run the intents command and choose which intents to generate:
cmnd intents "Financial Analysis"You’ll see a list of intents. Choose the ones you want to expand, and Command will:
- Generate content for each selected intent
- Save responses under the
Embedsfolder automatically - Link embeds in your document template instantly
Step 4: Visualize in Obsidian
If you’re using Obsidian, the Graph view shows all your linked embeds, creating a beautiful knowledge network. You can:
- Link related templates
- Enhance generated embeds with more intents
- Use Obsidian plugins to generate websites, PDFs, and more
Your creativity + Obsidian + Command = Magic!
Obsidian Integration
Command’s markdown-first approach makes it perfect for Obsidian users. Here’s how to set it up:
1. Initialize Command in Your Vault
cd /path/to/your/obsidian/vault
cmnd initThis creates:
command.ymlconfiguration file- Sample
IntentsandEmbedsfolders .env.local.examplefor API keys
2. Configure Your Workflow
Edit command.yml to match your Obsidian structure:
ask:
provider: claude
model: sonnet4-5
save: true
save-folder: Notes/Quick
refer-note-to-expand:
lookup-folder: Notes/Drafts
save-folder: Notes/Complete
model: opus4-1
intents:
lookup-folder: Templates
save-folder: Embeds
model: sonnet4-53. Create Templates
Use Obsidian’s template system alongside Command intents:
# {{title}}
Date: {{date}}
Tags: #draft #ai-generated
## Overview
[Brief description]
## Key Points
- Point 1
- Point 2
## Analysis
[To be expanded by Command]4. Expand and Link
Run Command to expand sections, then use Obsidian’s linking features:
refer note-to-expand "market-analysis-draft"The expanded note appears in your vault, ready for linking with [[wiki-links]].
VS Code Integration
Command works beautifully with VS Code for code-centric workflows:
1. Project Setup
Initialize Command in your project root:
cd /path/to/your/vscode/project
cmnd init2. Code Documentation Workflow
Create a refer-code-to-document section in command.yml:
refer-code-to-document:
lookup-folder: src
save-folder: docs
model: sonnet4-5
system: You are analyzing source code files.
Generate comprehensive documentation including purpose,
architecture, key functions, and usage examples.
temperature: 0.33. Generate Documentation
refer code-to-document "api-handlers.py"Command analyzes your code and generates detailed documentation in markdown format.
4. Test Case Generation
refer-code-to-test:
lookup-folder: src
save-folder: tests
model: sonnet4-5
system: Generate comprehensive test cases for this code,
including edge cases, error handling, and integration tests.
temperature: 0.2refer code-to-test "user-service.py"Advanced Workflow: Content Validation
Verify content generated by one LLM with validation from another model:
validate:
provider: claude
model: opus4-1 # Use Opus 4.1 for deep validation
max-tokens: 4000
temperature: 0.0 # Deterministic for validation
system: Validate the following content for accuracy,
completeness, and coherence. Suggest improvements.After generating embeds with cmnd intents, validate them:
cmnd validate "Financial Analysis"The diff is calculated on original and validated text, removing newlines, whitespace, and markdown formatting for similarity scoring. Use this to automate quality validation of generated content.
Practical Use Cases
Blog Writing Workflow
- Write brief outline in
Posts/drafts/ - Expand with
refer post-to-update "outline" - Validate with
cmnd validate - Review and publish
Time saved: 70% reduction in writing time while maintaining quality.
Research Workflow
- Collect sources in
Research/sources/ - Summarize with
refer paper-to-summarize - Generate synthesis with
cmnd intents "Research Project" - Create visualizations in Obsidian
Result: Comprehensive research synthesis in hours instead of days.
Documentation Workflow
- Write code with inline comments
- Generate docs with
refer code-to-document - Create API documentation with
cmnd intents "API Docs" - Validate technical accuracy with different model
Outcome: Always up-to-date, comprehensive documentation.
Privacy-First Workflows
For sensitive content, use local models:
refer-confidential-note:
lookup-folder: Private
save-folder: Private/Expanded
model: llama # Local Llama 3.1 via Ollama
provider: ollama # Fully local, zero cloud
system: Process this confidential information...Your sensitive data never leaves your machine.
Run Multiple Models Side by Side
Compare different models’ output by running them in parallel terminal windows:
Terminal 1 (Opus 4.1 - Creative):
cmnd config refer-post model opus4-1
refer post-to-update "content-strategy"Terminal 2 (Sonnet 4.5 - Analytical):
cmnd config refer-post model sonnet4-5
refer post-to-update "content-strategy"Terminal 3 (Local Llama - Fast Draft):
cmnd config refer-post model llama
cmnd config refer-post provider ollama
refer post-to-update "content-strategy"Compare outputs and choose the best result or combine insights from multiple models.
Audit Your Workflow
Track your content generation over time:
cmnd auditThe audit dashboard shows:
- Most used templates and intents
- Model performance by content type
- Token usage and cost analysis
- Saved files and their locations
Use these insights to optimize your workflow and reduce costs.
Get Started with Command Workflows
-
Install Command:
pip install command -
Initialize in your workspace:
cd /path/to/your/workspace cmnd init -
Configure your first workflow: Edit
command.ymlto match your needs -
Start creating:
ask "Help me create a blog post about AI workflows"
Visit navamai.com for comprehensive documentation, examples, and advanced workflow guides.
Command is part of Navam’s battle-tested AI toolkit. Explore our other products for complete AI-powered workflows across your entire development and knowledge management stack.
